Until now, you’ve mostly been testing bots with simulated transactions or basic unit tests. Lesson 11 is about deploying your agents on real testnets and preparing them for mainnet behavior. This includes using real chain data, monitoring for edge cases, and simulating real attack conditions.
Running unit tests is like experimenting in a lab; testing on mainnet is the real-world trial.
Why Test on Real Chains?
Testnets (like Sepolia) offer several advantages:
Access to real block timings and gas behaviors
Publicly deployed contracts that you can listen to
Exploit simulations without risking real funds
Even if your unit test passes, it might behave unpredictably in the wild:
Missed events due to block lag
High gas consumption
Bugs caused by blockchain chain reorganization
Out-of-order logs
Testing on-chain reveals these surprises early.
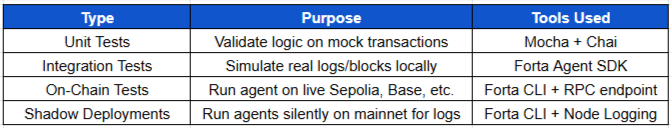
Types of Forta Tests
Run Agent on Sepolia
1. Get Sepolia RPC access
You can get a free endpoint from:
Alchemy
Infura
2. Modify forta.config.json
{
"jsonRpcUrl": "https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_KEY",
"chainId": 11155111,
"scanNodeUrl": "http://localhost:8920"
}3. Add a Sepolia-specific condition in your agent
if (tx.to === "0xYourContractAddress" && tx.value > ethers.utils.parseEther("5")) {
findings.push(Finding.fromObject({ ... })) }4. Run your agent
forta-agent runWatch for alerts and logs. You can simulate large transfers using faucets and test wallets.
Guidelines for Secure Mainnet Shadow Testing
“Shadow deployments” mean running your bot on real mainnet data, but without making its alerts public.
This lets you safely watch how your bot behaves in real conditions, without affecting users or triggering false alarms so that you can fix issues before going live.
To do it:
Set up your Forta scan node with
mainnetJSON-RPCRun your bot locally or on a private instance
Log findings without emitting them:
console.log("Would alert: Suspicious token transfer");This prepares you for:
Latency monitoring (tracking how fast your Forta bot responds to blockchain events, from event detection to alert emission)
Adjusting alert frequency (adjusting your bot to emit the right number of alerts, not too many, not too few)
Resource limits under real chain load (observing how your bot handles real-world conditions like: high transaction throughput, big blocks, memory or CPU usage spikes)
Use Case Example: Detecting Large Token Swaps
You can test this against Uniswap v3 pools:
if (log.address === "0xUniswapPool" && log.topics[0] === SwapTopic) {
const amountOut = decodeSwap(log.data);
if (amountOut > THRESHOLD) {
findings.push(Finding.fromObject({...}))
}
}
Push this bot live on Sepolia or Base testnet. Observe its behavior during high trading hours.
Testnet Fallback Best Practices
Always keep a backup JSON-RPC provider
Include
chainIdin your findings to separate mainnet/testnet logsLog your alerts to a file or console for offline analysis
Key Concepts Recap
Testing Forta bots on real testnets simulates production conditions without a real risk
Shadow deployments help adjust bots in real-time on mainnet
Use testnets to simulate known exploits, contract upgrades or wallet behaviors
This level of testing helps ensure your bot is reliable, responsive, and stable in real-world conditions
Every Forta Administrator should integrate testnet and mainnet testing in their CI workflow
Next lesson, we will explore alert routing and notifications, how to get real-time Forta alerts into Slack, Discord, and your internal dashboards.
Until next meditation,
The Blockchain Security Monk